|
|
@@ -0,0 +1,2467 @@
|
|
|
+<section id="v4l2-mbus-format">
|
|
|
+ <title>Media Bus Formats</title>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <table pgwide="1" frame="none" id="v4l2-mbus-framefmt">
|
|
|
+ <title>struct <structname>v4l2_mbus_framefmt</structname></title>
|
|
|
+ <tgroup cols="3">
|
|
|
+ &cs-str;
|
|
|
+ <tbody valign="top">
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>__u32</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry><structfield>width</structfield></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Image width, in pixels.</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>__u32</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry><structfield>height</structfield></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Image height, in pixels.</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>__u32</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry><structfield>code</structfield></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Format code, from &v4l2-mbus-pixelcode;.</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>__u32</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry><structfield>field</structfield></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Field order, from &v4l2-field;. See
|
|
|
+ <xref linkend="field-order" /> for details.</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>__u32</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry><structfield>colorspace</structfield></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Image colorspace, from &v4l2-colorspace;. See
|
|
|
+ <xref linkend="colorspaces" /> for details.</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>__u32</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry><structfield>reserved</structfield>[7]</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Reserved for future extensions. Applications and drivers must
|
|
|
+ set the array to zero.</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ </tbody>
|
|
|
+ </tgroup>
|
|
|
+ </table>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <section id="v4l2-mbus-pixelcode">
|
|
|
+ <title>Media Bus Pixel Codes</title>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>The media bus pixel codes describe image formats as flowing over
|
|
|
+ physical busses (both between separate physical components and inside SoC
|
|
|
+ devices). This should not be confused with the V4L2 pixel formats that
|
|
|
+ describe, using four character codes, image formats as stored in memory.
|
|
|
+ </para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>While there is a relationship between image formats on busses and
|
|
|
+ image formats in memory (a raw Bayer image won't be magically converted to
|
|
|
+ JPEG just by storing it to memory), there is no one-to-one correspondance
|
|
|
+ between them.</para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <section>
|
|
|
+ <title>Packed RGB Formats</title>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>Those formats transfer pixel data as red, green and blue components.
|
|
|
+ The format code is made of the following information.
|
|
|
+ <itemizedlist>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The red, green and blue components order code, as encoded in a
|
|
|
+ pixel sample. Possible values are RGB and BGR.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The number of bits per component, for each component. The values
|
|
|
+ can be different for all components. Common values are 555 and 565.</para>
|
|
|
+ </listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The number of bus samples per pixel. Pixels that are wider than
|
|
|
+ the bus width must be transferred in multiple samples. Common values are
|
|
|
+ 1 and 2.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The bus width.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>For formats where the total number of bits per pixel is smaller
|
|
|
+ than the number of bus samples per pixel times the bus width, a padding
|
|
|
+ value stating if the bytes are padded in their most high order bits
|
|
|
+ (PADHI) or low order bits (PADLO).</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>For formats where the number of bus samples per pixel is larger
|
|
|
+ than 1, an endianness value stating if the pixel is transferred MSB first
|
|
|
+ (BE) or LSB first (LE).</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ </itemizedlist>
|
|
|
+ </para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>For instance, a format where pixels are encoded as 5-bits red, 5-bits
|
|
|
+ green and 5-bit blue values padded on the high bit, transferred as 2 8-bit
|
|
|
+ samples per pixel with the most significant bits (padding, red and half of
|
|
|
+ the green value) transferred first will be named
|
|
|
+ <constant>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_RGB555_2X8_PADHI_BE</constant>.
|
|
|
+ </para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>The following tables list existing packet RGB formats.</para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <table pgwide="0" frame="none" id="v4l2-mbus-pixelcode-rgb">
|
|
|
+ <title>RGB formats</title>
|
|
|
+ <tgroup cols="11">
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="id" align="left" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="code" align="center"/>
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="bit" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="4" colname="b07" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="5" colname="b06" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="6" colname="b05" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="7" colname="b04" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="8" colname="b03" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="9" colname="b02" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="10" colname="b01" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="11" colname="b00" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <spanspec namest="b07" nameend="b00" spanname="b0" />
|
|
|
+ <thead>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Identifier</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Code</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry spanname="b0">Data organization</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Bit</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>7</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>6</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>5</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>4</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>3</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>2</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>1</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ </thead>
|
|
|
+ <tbody valign="top">
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-RGB444-2X8-PADHI-BE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_RGB444_2X8_PADHI_BE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1001</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-RGB444-2X8-PADHI-LE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_RGB444_2X8_PADHI_LE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1002</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-RGB555-2X8-PADHI-BE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_RGB555_2X8_PADHI_BE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1003</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-RGB555-2X8-PADHI-LE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_RGB555_2X8_PADHI_LE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1004</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-BGR565-2X8-BE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_BGR565_2X8_BE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1005</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-BGR565-2X8-LE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_BGR565_2X8_LE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1006</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-RGB565-2X8-BE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_RGB565_2X8_BE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1007</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-RGB565-2X8-LE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_RGB565_2X8_LE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x1008</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ </tbody>
|
|
|
+ </tgroup>
|
|
|
+ </table>
|
|
|
+ </section>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <section>
|
|
|
+ <title>Bayer Formats</title>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>Those formats transfer pixel data as red, green and blue components.
|
|
|
+ The format code is made of the following information.
|
|
|
+ <itemizedlist>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The red, green and blue components order code, as encoded in a
|
|
|
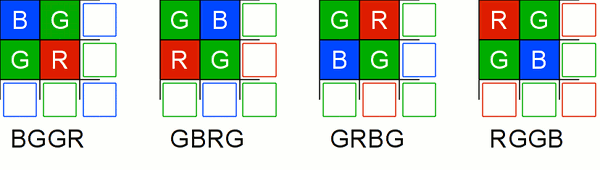
+ pixel sample. The possible values are shown in <xref
|
|
|
+ linkend="bayer-patterns" />.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The number of bits per pixel component. All components are
|
|
|
+ transferred on the same number of bits. Common values are 8, 10 and 12.</para>
|
|
|
+ </listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>If the pixel components are DPCM-compressed, a mention of the
|
|
|
+ DPCM compression and the number of bits per compressed pixel component.</para>
|
|
|
+ </listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The number of bus samples per pixel. Pixels that are wider than
|
|
|
+ the bus width must be transferred in multiple samples. Common values are
|
|
|
+ 1 and 2.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The bus width.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>For formats where the total number of bits per pixel is smaller
|
|
|
+ than the number of bus samples per pixel times the bus width, a padding
|
|
|
+ value stating if the bytes are padded in their most high order bits
|
|
|
+ (PADHI) or low order bits (PADLO).</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>For formats where the number of bus samples per pixel is larger
|
|
|
+ than 1, an endianness value stating if the pixel is transferred MSB first
|
|
|
+ (BE) or LSB first (LE).</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ </itemizedlist>
|
|
|
+ </para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>For instance, a format with uncompressed 10-bit Bayer components
|
|
|
+ arranged in a red, green, green, blue pattern transferred as 2 8-bit
|
|
|
+ samples per pixel with the least significant bits transferred first will
|
|
|
+ be named <constant>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SRGGB10_2X8_PADHI_LE</constant>.
|
|
|
+ </para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <figure id="bayer-patterns">
|
|
|
+ <title>Bayer Patterns</title>
|
|
|
+ <mediaobject>
|
|
|
+ <imageobject>
|
|
|
+ <imagedata fileref="bayer.pdf" format="PS" />
|
|
|
+ </imageobject>
|
|
|
+ <imageobject>
|
|
|
+ <imagedata fileref="bayer.png" format="PNG" />
|
|
|
+ </imageobject>
|
|
|
+ <textobject>
|
|
|
+ <phrase>Bayer filter color patterns</phrase>
|
|
|
+ </textobject>
|
|
|
+ </mediaobject>
|
|
|
+ </figure>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>The following table lists existing packet Bayer formats. The data
|
|
|
+ organization is given as an example for the first pixel only.</para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <table pgwide="0" frame="none" id="v4l2-mbus-pixelcode-bayer">
|
|
|
+ <title>Bayer Formats</title>
|
|
|
+ <tgroup cols="15">
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="id" align="left" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="code" align="center"/>
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="bit" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="4" colname="b11" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="5" colname="b10" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="6" colname="b09" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="7" colname="b08" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="8" colname="b07" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="9" colname="b06" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="10" colname="b05" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="11" colname="b04" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="12" colname="b03" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="13" colname="b02" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="14" colname="b01" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="15" colname="b00" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <spanspec namest="b11" nameend="b00" spanname="b0" />
|
|
|
+ <thead>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Identifier</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Code</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry spanname="b0">Data organization</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Bit</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>11</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>9</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>7</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>6</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>5</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>4</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>3</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>2</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>1</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ </thead>
|
|
|
+ <tbody valign="top">
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR8-1X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR8_1X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3001</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SGRBG8-1X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SGRBG8_1X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3002</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR10-DPCM8-1X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR10_DPCM8_1X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x300b</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SGBRG10-DPCM8-1X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SGBRG10_DPCM8_1X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x300c</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SGRBG10-DPCM8-1X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SGRBG10_DPCM8_1X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3009</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SRGGB10-DPCM8-1X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SRGGB10_DPCM8_1X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x300d</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR10-2X8-PADHI-BE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR10_2X8_PADHI_BE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3003</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR10-2X8-PADHI-LE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR10_2X8_PADHI_LE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3004</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR10-2X8-PADLO-BE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR10_2X8_PADLO_BE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3005</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR10-2X8-PADLO-LE">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR10_2X8_PADLO_LE</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3006</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR10-1X10">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR10_1X10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3007</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SGBRG10-1X10">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SGBRG10_1X10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x300e</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SGRBG10-1X10">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SGRBG10_1X10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x300a</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SRGGB10-1X10">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SRGGB10_1X10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x300f</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SBGGR12-1X12">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SBGGR12_1X12</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3008</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>11</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>10</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>b<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SGBRG12-1X12">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SGBRG12_1X12</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3010</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>11</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>10</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SGRBG12-1X12">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SGRBG12_1X12</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3011</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>11</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>10</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>g<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-SRGGB12-1X12">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_SRGGB12_1X12</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x3012</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>11</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>10</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>r<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ </tbody>
|
|
|
+ </tgroup>
|
|
|
+ </table>
|
|
|
+ </section>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <section>
|
|
|
+ <title>Packed YUV Formats</title>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>Those data formats transfer pixel data as (possibly downsampled) Y, U
|
|
|
+ and V components. The format code is made of the following information.
|
|
|
+ <itemizedlist>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The Y, U and V components order code, as transferred on the
|
|
|
+ bus. Possible values are YUYV, UYVY, YVYU and VYUY.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The number of bits per pixel component. All components are
|
|
|
+ transferred on the same number of bits. Common values are 8, 10 and 12.</para>
|
|
|
+ </listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The number of bus samples per pixel. Pixels that are wider than
|
|
|
+ the bus width must be transferred in multiple samples. Common values are
|
|
|
+ 1, 1.5 (encoded as 1_5) and 2.</para></listitem>
|
|
|
+ <listitem><para>The bus width. When the bus width is larger than the number of
|
|
|
+ bits per pixel component, several components are packed in a single bus
|
|
|
+ sample. The components are ordered as specified by the order code, with
|
|
|
+ components on the left of the code transferred in the high order bits.
|
|
|
+ Common values are 8 and 16.</para>
|
|
|
+ </listitem>
|
|
|
+ </itemizedlist>
|
|
|
+ </para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>For instance, a format where pixels are encoded as 8-bit YUV values
|
|
|
+ downsampled to 4:2:2 and transferred as 2 8-bit bus samples per pixel in the
|
|
|
+ U, Y, V, Y order will be named <constant>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_UYVY8_2X8</constant>.
|
|
|
+ </para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <para>The following table lisst existing packet YUV formats.</para>
|
|
|
+
|
|
|
+ <table pgwide="0" frame="none" id="v4l2-mbus-pixelcode-yuv8">
|
|
|
+ <title>YUV Formats</title>
|
|
|
+ <tgroup cols="23">
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="id" align="left" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="code" align="center"/>
|
|
|
+ <colspec colname="bit" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="4" colname="b19" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="5" colname="b18" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="6" colname="b17" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="7" colname="b16" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="8" colname="b15" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="9" colname="b14" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="10" colname="b13" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="11" colname="b12" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="12" colname="b11" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="13" colname="b10" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="14" colname="b09" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="15" colname="b08" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="16" colname="b07" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="17" colname="b06" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="18" colname="b05" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="19" colname="b04" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="20" colname="b03" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="21" colname="b02" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="22" colname="b01" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <colspec colnum="23" colname="b00" align="center" />
|
|
|
+ <spanspec namest="b19" nameend="b00" spanname="b0" />
|
|
|
+ <thead>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Identifier</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Code</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry spanname="b0">Data organization</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>Bit</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>19</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>18</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>17</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>16</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>15</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>14</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>13</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>12</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>11</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>9</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>7</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>6</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>5</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>4</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>3</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>2</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>1</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0</entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ </thead>
|
|
|
+ <tbody valign="top">
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-Y8-1X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_Y8_1X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2001</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-UYVY8-1_5X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_UYVY8_1_5X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2002</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-VYUY8-1_5X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_VYUY8_1_5X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2003</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YUYV8-1_5X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YUYV8_1_5X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2004</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YVYU8-1_5X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YVYU8_1_5X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2005</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-UYVY8-2X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_UYVY8_2X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2006</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-VYUY8-2X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_VYUY8_2X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2007</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YUYV8-2X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YUYV8_2X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2008</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YVYU8-2X8">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YVYU8_2X8</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2009</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-Y10-1X10">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_Y10_1X10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x200a</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YUYV10-2X10">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YUYV10_2X10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x200b</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YVYU10-2X10">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YVYU10_2X10</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x200c</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-UYVY8-1X16">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_UYVY8_1X16</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x200f</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-VYUY8-1X16">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_VYUY8_1X16</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2010</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YUYV8-1X16">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YUYV8_1X16</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2011</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YVYU8-1X16">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YVYU8_1X16</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x2012</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>-</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YUYV10-1X20">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YUYV10_1X20</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x200d</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row id="V4L2-MBUS-FMT-YVYU10-1X20">
|
|
|
+ <entry>V4L2_MBUS_FMT_YVYU10_1X20</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>0x200e</entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>v<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ <row>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>y<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>9</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>8</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>7</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>6</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>5</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>4</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>3</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>2</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>1</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ <entry>u<subscript>0</subscript></entry>
|
|
|
+ </row>
|
|
|
+ </tbody>
|
|
|
+ </tgroup>
|
|
|
+ </table>
|
|
|
+ </section>
|
|
|
+ </section>
|
|
|
+</section>
|